|
Customs of Septuagesima & Lent X Pre-Lenten (Septuagesima) Customs
As Septuagesima (Latin for "seventy") is seventy days before Easter, it typologically commemorates the seventy years of exile spent by the Jews in Babylon. As Psalm 136 attests, God's chosen people did not deem it fit to sing their joyous songs from Sion during the Babylonian exile, and neither do Catholics during theirs. The joyful "Alleluia" is thus laid to rest for seventy days until it rises again in the Easter Vigil. As mentioned elsewhere, this dismissal, or depositiio, of the Alleluia can take place formally in a special ceremony. After the Saturday office of None or at some point of the afternoon on the day before Septuagesima Sunday, the choir gathers in the church where it carries a plaque or banner bearing the word "Alleluia" through the church as it sings the touching hymn, "Alleluia, dulce carmen" (part of which is quoted elsewhere). It is then solemnly "buried" in some place in the church. In the Middle Ages this procession could become quite elaborate. Sometimes the "Alleluia" plaque would be in the shape of a coffin, while in parts of France, a straw man with the word "Alleluia" was even burned in effigy in the churchyard. A simpler ceremony based on the same principles, however, can easily be held in one's home or parish.
As mentioned elsewhere, it was customary for some Christians to voluntarily begin fasting in preparation for the Great Fast of Lent. Their fasts would become progressively more ascetic, culminating in the abstinence of meat beginning on the Thursday before Ash Wednesday. The name for this period, which ends the day before Ash Wednesday, is "Carnival," from the Latin carne levarium, meaning "removal of meat."
It might sound odd that during the period of "Carnival" there occurs some of the most decadent feasting of the liturgical year. There is, however, a pious (if not somewhat convoluted) logic behind this consumption. Because not only meat but lacticinia (dairy products) were originally prohibited during Lent, Christians knew that they had to eat these foods before Ash Wednesday or they would spoil. The last days before Lent were thus spent in eating copious amounts of fat dishes. From this necessity comes England's famous Shrove Tuesday Pancakes and northern England's Collop Monday (a collop is made of sliced meat and eggs fried in butter). This also gave rise to the most famous (or infamous, depending on your point of view) Christian party of all: Mardi Gras. Mardi Gras, or "Fat Tuesday," is the French celebration of the final day before Lent. In this country it is associated mostly with the Cajun and Creole cuisine of New Orleans, two culinary traditions that provide a myriad of spicy, delicious dishes. One of the |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
more interesting customs of the New Orleans Mardi Gras is the baking of a King's Cake, in which is placed a small doll of the Infant Jesus. The person whose piece of cake has the doll must provide the cake for next year's party. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Because the Shrovetide celebrations became prone to excess and scandal, Pope Benedict XIV instituted in 1748 the Forty Hours of Carnival, especially in those areas prone to such reveling. During this devotion the Blessed Sacrament is exposed during the day and Benediction held in the evening.
1. The Great Fast | 2. Asceticism | 3. Good Works | 4. Mourning & Veiling | 5. Confession & Communion | 6. Stations of the Cross | 7. Mid-Lent | 8. Passiontide | 9. Holy Week/Triduum
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Of all the observances of Lent, the chief among these is the Great Fast. So intertwined are the two, in fact, that the Fathers of the Church sometimes used the terms interchangeably. This solemn obligation is believed to be of Apostolic origin and takes its precedent, as we mentioned above, from the examples of Moses, Elias, and Jesus Christ. The Great Fast used to consist of both abstinence and fasting. Christians were expected to abstain not only from flesh meat, but from all things that come from flesh, e.g. milk, cheese, eggs, and butter. Eastern rite Christians still observe this practice, while the Western church gradually kept only abstinence from meat (reference to all lacticinia, or "milk foods," was dropped in the 1919 Roman Code of Canon Law). Both East and West, however, agree on the importance of fasting. Originally this meant taking only one meal a day, though the practice was modified over the centuries. The preconciliar practice in the U.S. was for all able-bodied Catholics ages 21 to 60 to have one full meal a day which could include meat, and two meatless meals which together could not equal one full meal. Snacking between meals was prohibited, though drinking was not. Ash Wednesday, Fridays and the Ember Days were days of total abstinence from meat, while Sundays were completely exempted from all fasting and abstaining. The idea behind the Great Fast -- as well as other periods of fasting -- is that by weakening the body it is made more obedient to the soul, thereby liberating the soul to contemplate higher things. St. Augustine gives perhaps the best example: if you have a particularly high-spirited horse, you train it at the times when it is too weak to revolt. It is our opinion that this venerable practice should still be taken seriously. Even though current ecclesiastical law has reduced the fast from forty days to two and eliminated the thirty-three days of partial abstinence, this does not mean that observing the Great Fast is not salubrious or praiseworthy. This said, however, the Great Fast should not be adhered to legalistically. In the words of St. John Chrysostom: "If your body is not strong enough to continue fasting all day, no wise man will reprove you; for we serve a gentle and merciful Lord who expects nothing of us beyond our strength." Since Lent recapitulates time spent in the desert, other forms of asceticism have accrued to its observance. Unessential travel and diversion are discouraged. In former times, certain forms of entertainment, such as live theatre and secular music, were banned, as was the holding of court. Weddings were also forbidden in the early Church; even after this changed, the Solemn Nuptial Blessing could not be given during a Lenten wedding. Finally, married couples were once admonished to abstain from conjugal relations during this time (as they were admonished to do during all solemn fasts and feasts). Again, the principle is the same: withdrawal from the preoccupations of the flesh in order to focus on the spirit. Lent is traditionally considered a particularly good time for performing corporal works of mercy (e.g., almsgiving, peacemaking, etc.). The importance of supplementing ascetical denial with active virtues is underscored in the Gospel for the Third Sunday of Lent (Luke 11.14-28), in which a man who has had a demon exorcized from him later becomes repossessed by the demon and seven other unclean spirits. Christ's point seems to be that holy practices such as fasting do indeed remove bad things from one's soul, but this is ultimately to no avail if the soul is not then filled with good things. This understanding is also operative in the Collect for the First Sunday of Lent: O God, who by the yearly Lenten observance dost purify Thy Church, grant to Thy household that what they strive to obtain from Thee by abstinence, they may achieve by good works. Akin to the asceticism of Lent is its mournful tone. The Church is traditionally draped in purple or black, its organ silenced, and its altar bereft of any flowers. At home medieval Catholics would avoid frivolity or hilarity, and would wear black during either Holy Week or Good Friday. There is a special mourning custom that also begins on Passion Sunday and ends when the Gloria is sung during the Easter Vigil Mass: covering all sacred images (crucifixes, statues, etc.) with purple cloth in both church and home. This might seem counterintuitive, since one would expect to gaze at a crucifix more during the season when the Passion is being considered. Yet the Roman rite teaches by absence as well as by presence. In an odd way, being denied access to the sacred images alerts you to their presence all the more, in the same way that not having the sacrifice of the Mass on the one day you would expect it the most, i.e., Good Friday, makes one all the more aware of the Sacrifice that took place on that day. Covering sacred images also adds immensely to the sense of sorrow and compunction that should naturally accompany this somber period. One of the Precepts of the Church is to receive the sacraments of Penance and Holy Communion at least once a year, during Lent or Paschaltide. As mentioned above, Catholics once dedicated the three days prior to Lent as a special time to go to confession. Shrovetide arose from the desire to prepare for the holy asceticism of the Great Fast. Once Lent begins, however, confession should still be sought out: since Lent is a time for frequent and frank examinations of conscience, confession is a sacrament that should be liberally taken advantage of during this time. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
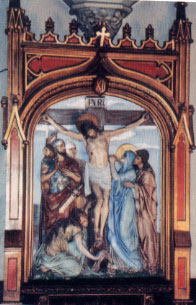
Though technically only the last fourteen days of Lent explicitly consider the sufferings of our Lord, the Stations of the Cross (a.k.a. the Way of the Cross) have long been a popular Lenten devotion for any or all of the forty days (though they tend to be done on Fridays). These fourteen scenes from the via dolorosa, the sorrowful path that Christ took while carrying His cross to Golgotha, help direct one's heart to the mysterium fidei of our Lord's selfless sacrifice. |
Twelfth Station of the Cross, Holy Trinity Church |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Mid-Lent, the week from the Wednesday before to the Wednesday after Laetare Sunday, is a note of joy within the context of sorrow. The perfect symbol of this complex emotion is the rose vestments worn on Laetare Sunday instead of penitential purple or exultent white. Rose stands somewhere in between, as a sort of joyous variation of purple. The last day of Mid-Lent is when catechumens would learn the Apostles' Creed for the first time; the days leading up to that great revelation were thus for them a cause for gladness. This spirit eventually permeated to the rest of the community as "a measure of consoling relaxation... so that the faithful might not break down under the severe strains of the Lenten fast but may continue to bear the restrictions with a refreshed and easier heart" (Pope Innocent III (d. 1216)). Mid-Lent customs predominantly involve pre-Christian celebrations concerning the "burial" of winter, where flower decorations and the like betoken the joyous end of the cold and dark. There are also customs involving either matchmaking or announcing the engagements of young couples. In either case, a joyous meal is celebrated during this time. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
In England Laetare Sunday came to be known as "Mothering" Sunday because it was the day that apprentices and students were released from their duties to visit their mother church, i.e., the church in which they had been baptized and brought up. This custom tied into the theme of Mother Jerusalem |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
The main custom for Passiontide, as mentioned above, is the veiling of all sacred images in home and church with purple cloth. This custom originated in ancient times, when the images in the papal chapel of the Vatican were covered after the words of the Passion Sunday Gospel, "Jesus hid himself and went out of the temple" (Jn 8.59), were pronounced.
Spring Cleaning. Just as the Hebrews cleaned and swept the whole house in preparation for the Pasch (Passover), so too is there an ancient custom in Christianity that the first three weekdays of Holy Week be a time for the year's most thorough cleaning. Everything is to be scrubbed and polished, and all work is to be completed by Wednesday evening (in time for Tenebrae). Attending Tenebrae. Tenebrae consists of the divine office of Matins and Lauds for Maundy Thursday. It is generally held on the night of "Spy Wednesday" of Holy Week, so-called because it is believed to be the night on which Judas Iscariot betrayed our Lord. The service thus explores the nature of Judas' betrayal, the mental anguish of our suffering Lord, and the desecration of what was once holy and beautiful. Its ceremonies include the use of a "hearse," a triangular candelabrum that holds fifteen candles which are successively existinguished during the liturgy until the entire church is enveloped in darkness. Only one candle remains lit at the end, which is hidden by the Epistle side of the altar before the Miserere is chanted. The service concludes with a banging noise, followed by silence. The extinction of the fourteen candles calls to mind the fourteen holy men mentioned in the Bible who, from the foundation of the world to the very threshold of Christ's coming, were slain by their own wicked brethren. The hiding of the fifteenth candle, on the other hand, signifies the murder and resurrection of Christ Himself, while the banging noise commemorates the confusion of nature when its Creator died (Mt. 27.51). |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Attending Maundy Thursday Mass. There were originally three separate Masses for Maundy Thursday. The first, no longer in use, is the Mass of Remission, whereby the public penitents who had been doing special penance during Lent were received back into the Church. The second is the Chrism Mass, when the bishop blesses the holy oils to be used for the year. The third is the evening Mass of the Lord's Supper, in which the Church celebrates the institution of the Eucharist and the priesthood. The special ceremonies for this exultant Mass (the Gloria returns and white vestments are used) include the priest's washing the feet of twelve men, the removal of the Eucharist to the Altar of Repose, and the stripping of the altars. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
The Maundy Thursday Vigil. After the Blessed Sacrament is "laid to rest" in a special tabernacle on the Altar of Repose, it is customary for the church to stay open all night and for private devotion to take place. A variation of this custom is to visit seven such shrines during the night in imitation of the Sette Chiese of the Roman Stations (see Stations). This custom was quite popular in American cities like Boston until the late 1960s. "Clean" Thursday Customs. Because it was the day that penitents and catechumens were cleansed of their sins (and allowed to bathe again), Maundy Thursday is known in some parts of the world as "Clean" Thursday. The idea of cleanliness also extended to the rest of the faithful. In a time when bathing did not happen every day, Clean Thursday became the occasion for thoroughly cleansing the body in preparation for Easter. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
There is also a charming legend that after the bells are rung for the Gloria during the Mass of the Last Supper, "they fly to Rome" where -- depending on who is telling the story -- they either are blessed by the Pope and sleep on the roof of St. Peter's Holy Saturday night, or are given Easter eggs to return with them on Sunday morning. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Attending the Good Friday Service. The sacrifice of the altar is not offered on the day commemorating the sacrifice of the cross, and though communion may be distributed, the faithful are discouraged from receiving it without good reason. Instead, a mournful service is conducted. The priest, vested in black, reads several passages from the Bible, including the Passion account from the Gospel of John. Afterwards, the "Solemn Prayers" or "Collects" are offered on behalf of all classes of men, from the Church to the heathen. This is followed by the veneration of the cross, during which time the dolorous "Reproaches" are chanted. The service concludes with the "Mass of the Presanctified," a solemn communion rite. Forty Hours' Devotion: It is traditionally believed that the duration of time from Christ's death until His Resurrection is forty hours, from 3 p.m. on Good Friday until 7 a.m. Easter Sunday. As early as the 100s it was customary for some of the faithful to fast and keep vigil during this entire period. Other Good Friday Customs. If a devotion of forty hours could not be done, many Catholics observed Good Friday as a day of austerity as best they could. Fasting more than was required was common. Attending the Three Hours' Devotion, or Seven Last Words of Christ, from 12 p.m. to 3 p.m. (the hours our Lord hung upon the cross), has also been popular. Liturgically speaking, this is a relatively new observance, begun in Peru in the early 1700s, but it is a very effective one. An older tradition that has lamentably been forgotten, on the other hand, is that of the Holy Sepulchre, a special shrine set up to house either the Blessed Sacrament or a crucifix which the faithful could visit on Good Friday and Holy Saturday.
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||